Also in this category
View more in Connectivity for Remote NetworksConnectivity for Remote Networks
A guide to cellular antennas: Resolving rural connectivity
Updated on May 6, 2025

Cellular antennas are critical connectivity devices for rural enterprises and businesses
Virtually every business today has integrated the wireless-based technologies they need for everyday business functions. For example, retailers have leveraged wireless networks and cloud computing for online inventory management and point-of-sale (PoS) machines. Hospitals and health clinics use wireless networks to provide remote health care services via online telehealth systems. Mining operators use wireless networks to support automatic monitoring of environmental conditions in mines that alert miners instantly to dangerous gases or potential cave-ins.
All these systems need highly reliable internet connections. Without reliable connectivity, PoS machines, telehealth services, and remote monitoring equipment are mere hypotheticals.
For businesses or enterprises operating in rural or remote areas, crowded commercial zones, or just in areas prone to bad weather that impact satellite signals, maintaining reliable, high-quality connectivity can make or break their success. One of the most powerful devices available that can ensure any business maintains a reliable connection in a rural location is a cellular antenna. To get the most out of these antennas, it's important to know how to properly add them to your current network setup, from initial deployment to regular upkeep.
Step 1: Evaluate optimal cellular antenna type based on connectivity needs
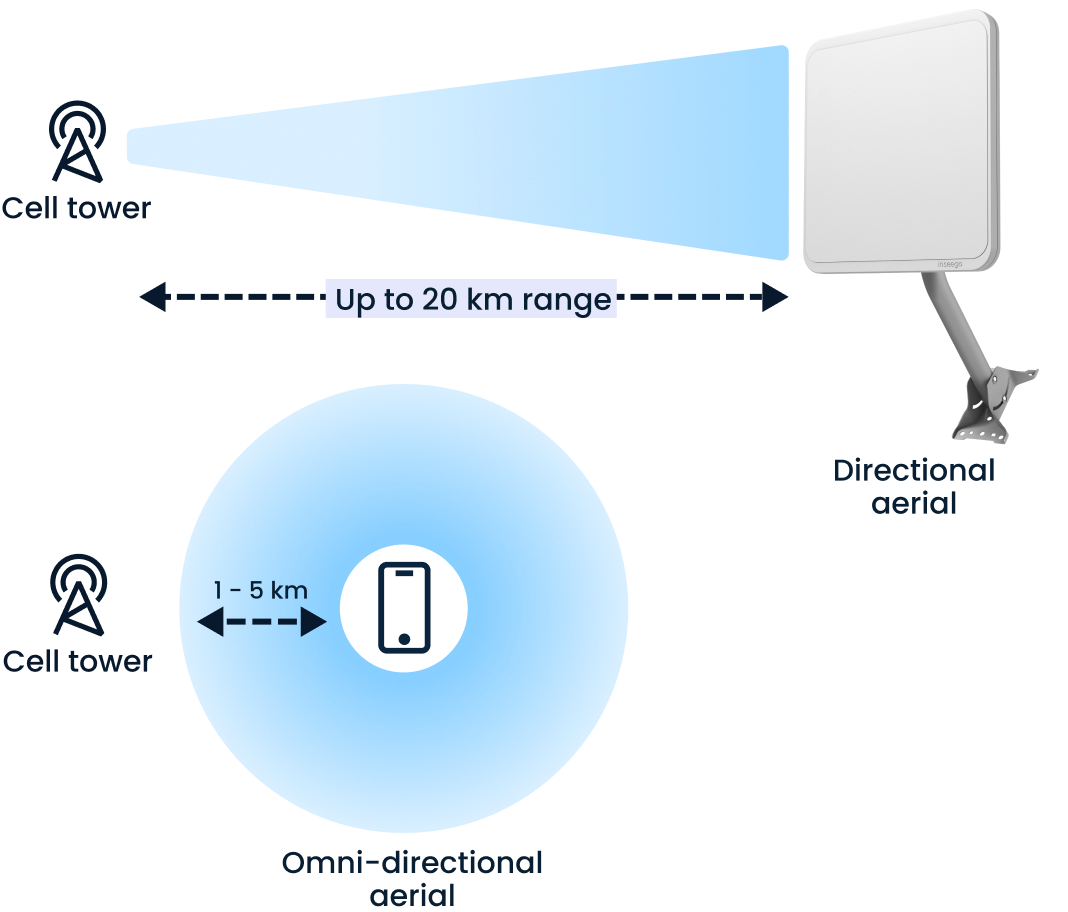
First and foremost, it’s important to understand that there are several types of cellular antennas, each of which has different attributes that make it better suited for specific use cases and industries. In general, there are three types: omnidirectional, directional, and panel.
Omnidirectional antennas are exactly what they sound like. They are designed to capture a cellular signal from any direction, making them extremely reliable at capturing signals that come from unpredictable and dynamic directions. These antennas are easier to deploy as they are less sensitive to alignment requirements and best suited for urban environments, where cellular signals tend to ricochet unpredictably around buildings and other tall obstacles.
Directional cellular antennas aren’t simply more limited omnidirectional antennas. These devices are built to capture a signal coming from a cell tower in a known direction and do so more effectively than omnidirectional antennas. While this makes them more sensitive to alignment requirements during setup, it also means they’re extremely good at capturing even weak signals from known directions, making them an excellent choice in rural and remote areas.
Finally, there are panel antennas. These are large, flat antennas that are typically mounted on walls or other flat surfaces to provide optimal coverage. Because of their size, they’re better at mitigating the effects of signal diffusion and diffraction, which can be caused by atmospheric moisture over long distances, and obstacles such as trees and buildings. This makes them a popular choice for enterprises that need consistent internal signal coverage irrespective of prevailing conditions.
Step 2: Conduct a site survey before placement and mounting
Next, it’s crucial to consider how the antenna or antennas will be deployed. Finding the optimal location and setup for your cellular antenna is essential for maximizing device performance and signal quality.
This process should begin with a site survey. Signal strength can vary greatly even in a small area, such as a rooftop where an antenna may be deployed, and as such it’s very important to find the best possible position before deploying. Using a mobile tool that allows you to capture cellular signal strength in dBm in real time as you do a site walkthrough is one of the most straightforward and effective ways to accurately capture relative signal strength.
It's also worth investigating not just the strength of the signal at different points but also the stability of that signal. One placement might have a higher maximum signal strength but a lower average signal strength if it fluctuates over the course of a day. Taking the time to evaluate both can ensure your business doesn’t waste time and money deploying antennas where signal strength just happened to be briefly higher during the survey.

Finally, the actual physical mechanism used to mount the antennae matters and can make a difference. Available mounting hardware includes roof mounts, pole mounts, magnetic mounts, and towers. Roof mounts are excellent for installations that require antennas to have a high vantage point, while pole mounts are often a good choice for omnidirectional antennas, as wall and roof mounts impede incoming signals. Magnetic mounts are extremely flexible as they are impermanent, allowing an enterprise to move an antenna if signal strength changes by location over time. Tower mounts are essentially a more extreme version of a roof mount, providing greater height to improve signal quality but adding to the cost and complexity of deployment.
Step 3: Ensure legal and regulatory compliance for deployment
Despite the ubiquity of wireless cellular connections and antennas, the deployment and installation of wireless antennas are thoroughly regulated, both at the local level and by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Signal interference can be a significant issue, particularly to radio or television transmission, which are often used by local, state, and federal governments to issue critical communications. FCC regulations define acceptable limits to ensure devices that generate radio frequencies do not do so in a way that generates harmful interference.
FCC regulations define Class A devices, which are those marketed exclusively in business, commercial, and industrial environments, and Class B devices, which are marketed for use anywhere, though they’re sometimes considered consumer-focused devices. Ensuring any wireless solution you integrate is compliant with the regulations for its respective device class is critical.
Regulatory compliance, however, does not guarantee that interference will not occur after installation. If the equipment causes harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, try to correct the interference using one or more of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
- Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help.
Step 4: Device maintenance post-deployment
As previously noted, connectivity issues can sometimes only be identified once a wireless antenna has been deployed. Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring longevity and optimal performance after installation.
The old adage that an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure is true for device maintenance. Regular inspections should be done on connectors and cables, which can be degraded by both inclement weather and simply by time. Rain, wind, hail, but also simple exposure to moisture and regular use can cause these elements to fray, corrode, or otherwise degrade over time, affecting both their functionality and safety.
The mounting hardware and mast of the antenna should also be inspected regularly, as they face many of the same issue as connectors and cables, including rusting and loosening that can affect structural integrity.
The grounding system should also be inspected regularly. Should it become compromised in any way, your system will be vulnerable to lightning damage and other electrical issues.
Finally, the antennas themselves may be affected by environmental conditions over time. Dirt, dust, and bird droppings can accumulate on the antenna, impacting its performance. Regularly clean the antenna to ensure unobstructed signal reception.
Step 5: Proactively troubleshoot to optimize device performance
Beyond simply ensuring that antennas are intact and undamaged, it’s important to continue to monitor performance and address issues as they arise. This can be as simple as turning off the antennas, waiting a few minutes, then turning them back on again, and ensuring all connectors and cables are tightly fastened and securely plugged in.
Signal quality can degrade over time for several reasons, not all of which are related to proper maintenance of the physical device. As with many other modern devices, many cellular antennas have associated firmware and software that may need to be updated to ensure devices continue to perform and to fix any bugs that may arise.
New installations of cellular equipment elsewhere, or even construction of buildings or tree growth, can also affect signal quality. Using a signal meter to evaluate the signal quality, particularly once performance issues have been noted, can help your enterprise identify possible solutions. This may necessitate moving antennas to a new position to avoid the interference, adjusting the directionality of the antennas if high winds or physical impacts have altered it, or if signal strength is simply better at a new orientation. It’s also possible a solution is as simple as turning off other nearby devices that are interfering with signal quality.
Inseego offers industry-leading wireless connectivity solutions
Effectively deploying cellular antennas is crucial to leveraging reliable, high-speed broadband internet to power value-add modern technologies.
Inseego is an industry leader in wireless cellular connectivity solutions, with numerous industry firsts delivering high-quality, reliable 4G LTE and 5G connections to enterprises in urban and remote environments.
The Inseego Mobile app allows you to conduct a signal strength survey in real time from your phone, ensuring initial antenna placement is optimal while also making it fast and easy to evaluate signal quality on an ongoing basis.
The Inseego Wavemaker Pro FW3000 is a high-performance 5G/LTE cellular outdoor antenna designed to deliver powerful connectivity solutions. This device features wideband reception, efficiently covering low MHz frequencies up to high-frequency bands. It provides a high-gain capability with an impressive boost of up to 11 dBi and a connectivity range extending as much as 10 kms from a cellular tower.
Engineered for low-profile installations, the FW3000 is also highly suitable for residential and commercial buildings. Its compatibility with major carriers like Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile ensures broad usability across different networks. Additionally, it supports PoE, only requiring you to use an ethernet cable for both power and data transfer.
Enhance your connectivity with one of the leading options available, ensuring robust and consistent performance in even the most challenging environments.
For detailed insights, contact us today.
Talk to our experts!
Set your customers or business up with the fastest, most secure, easiest, most reliable fixed wireless solutions.
Is your current internet connection meeting your business needs?
Even though your current connection is meeting your needs 5G cellular is also an affordable way to provide a back-up internet connection if your primary connection goes down.
Inseego outdoor antennas can support dual SIM cards for multi-carrier failover and ultimate reliability.
How is your connection letting you down?
What is your current connection type?
Do you get cell signal at your business?
Who is your current network provider
We've got a solution
A 5G cellular connection is a great way provide extra resilience to you business. This means if your primary connection goes down, any part of your business that relies on connectivity can carry on uninterrupted.
Even if you get a weak or almost no signal from your mobile phone, you can still get a great connection thanks to the powerful, directional antenna inside the FW2000.
5G cellular plans are affordable, with internet options from $50 - $100 per month, from the leading network providers.
What are your details?
How can we contact you?
Thanks, we've got your request
We’re excited to share our 5G connectivity solutions with you.
Check your email now for a confirmation message. Then a member of our team will send a personalised message within 1 business day to arrange a suitable time to have an in-depth one on one consultation.

5G Outdoor FW2000



Did you know?

5G Outdoor FW2000

Did you know?
Our hugely experienced team are located across the USA.
We’ll connect you with the Inseego team member nearest to you.
What happens next?
We aim to contact you via email within 1 business day to arrange a suitable to time for a detailed discussion of your needs.

