Also in this category
View more in 5G5G
4G LTE vs. 5G: How do they compare?
Updated on December 4, 2025

For years, 4G LTE (Long-Term Evolution) networks served as the bedrock of mobile communication, offering reliable service. It digitized our mobile experience, but it was built on a "one-size-fits-all" architecture that eventually strained under the demand for greater speed and capacity.
5G, the fifth generation of mobile network technology, is more than just a faster signal; it is a fundamental shift in network architecture designed to handle a massive surge in connected devices. Its speed over other wireless networks, its low latency, and real-time communication capabilities make it an ideal choice for connected devices that demand quick, millisecond-level responses, such as self-driving cars, virtual reality, and other similar applications. This means 5G technology promises to revolutionize how we use the internet, and it has the potential to revolutionize how we use the internet of things (IoT).
Core performance metrics that make 5G superior: Speed, latency, and the radio
The most immediate comparison between 4G and 5G rests on three measurable advantages:
- Speed: 4G LTE's peak download speed generally tops out at around 100 Mbps (Megabits per second), whereas 5G can theoretically deliver speeds up to 20 Gbps (Gigabits per second).
- Latency: 4G LTE typically has a latency between 50 and 100 milliseconds. 5G is engineered to achieve latency as low as 1 millisecond. This ultra-low latency is the key to real-time communication for critical applications.
- Technology: 5G replaces the previous radio technology with 5G New Radio (5G NR), built specifically to leverage higher-frequency spectrum bands and advanced signal processing.
How 5G is built to enable its superiority to 4G LTE
The capacity revolution: Massive MIMO and intelligent beamforming
The technologies that enable 5G to handle vastly more users and devices simultaneously, its capacity, are perhaps its most profound improvement over 4G LTE.
Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output)
If a 4G LTE cell tower has a limited number of antennas (typically up to four), a 5G base station is equipped with a huge array, often 64, 128, or more. This is Massive MIMO. It acts like a massive set of traffic lanes, allowing the station to transmit and receive dozens of independent data streams simultaneously on the same frequency band, effectively multiplying the network's total capacity. This is why 5G can support up to 1 million devices per square kilometer, significantly more than 4G.
Intelligent beamforming
Beamforming is the mechanism that directs the signal precisely. Instead of broadcasting a signal broadly like 4G, 5G employs intelligent beamforming software to dynamically calculate the location of a device and direct a focused, narrow beam of radio energy specifically toward it. This directed energy:
- Reduces Interference: By focusing the signal only where needed, it avoids wasting power and minimizes interference for other users.
- Increases Consistency: It overcomes the natural range limitations of high-frequency 5G signals, improving the effective coverage and signal quality for the individual user.
Different 5G types cover all use cases
The applications and benefits of 5G are almost limitless due to the exponential difference in 5G’s speed and capacity compared to previous generations of networking technology. There are three types of 5G, each of which is best suited to different use cases:
- High-band 5G, also referred to as millimeter wave or mm-wave, uses high-frequency bands, typically between 24 GHz and 52 GHz, to deliver ultra-fast download speeds. It offers the fastest data rates, but generally only covers short distances.
- Mid-band 5G uses frequencies between 3 GHz and 24 GHz, offering better coverage and improved latency over high-band 5G. This type of 5G is the preferred option for most telecoms, as it offers a good balance between speed and coverage.
- Low-band 5G uses frequencies below 1 GHz. It offers the best coverage, with speeds comparable to those of 4G LTE, and is the most popular 5G option for carriers in the United States.
5G offers opportunities across multiple industries & verticals
The three varieties of 5G make it applicable to a broad variety of verticals, both for enhancing current operations and enabling new opportunities.
For example:
- Automotive: 5G is expected to revolutionize the automotive industry by providing faster and more reliable connections for self-driving cars, improved navigation, and real-time traffic updates.
- Healthcare: 5G will enable healthcare providers to transmit high-resolution images and vital signs quickly, improving the accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
- Retail: 5G will enable faster checkout, improved inventory tracking, and real-time location-based marketing.
- Manufacturing: 5G will enable higher precision, more automation, and faster communication between machines in the manufacturing process.
- Education: 5G will allow for more interactive and immersive learning experiences, such as virtual reality and augmented reality.
- Agriculture: 5G will enable more precise farming techniques, such as automated irrigation, soil monitoring, and crop monitoring.
Inseego helps you take advantage of 5G
Overall, 5G networks offer a significant upgrade over 4G LTE networks, and they have the potential to revolutionize the way we use the internet, our mobile devices, and IoT devices across multiple industries.
But to do so, enterprises will need devices that allow them to leverage the right type of 5G for their operation. Rural enterprises may want to take advantage of low-band 5G using wireless cellular routers. Indoor, urban enterprises may want to look at fixed wireless devices that allow easy deployment of high-power 5G wherever it's needed.
Learn more about fixed wireless accessContact us today to learn about which devices would most benefit your business.
Talk to our experts!
Set your customers or business up with the fastest, easiest, most reliable fixed wireless solutions.
Is your current internet connection meeting your business needs?
Even though your current connection is meeting your needs 5G cellular is also an affordable way to provide a back-up internet connection if your primary connection goes down.
Inseego outdoor antennas can support dual SIM cards for multi-carrier failover and ultimate reliability.
How is your connection letting you down?
What is your current connection type?
Do you get cell signal at your business?
Who is your current network provider
We've got a solution
A 5G cellular connection is a great way provide extra resilience to you business. This means if your primary connection goes down, any part of your business that relies on connectivity can carry on uninterrupted.
Even if you get a weak or almost no signal from your mobile phone, you can still get a great connection thanks to the powerful, directional antenna inside the FW2000.
5G cellular plans are affordable, with internet options from $50 - $100 per month, from the leading network providers.
What are your details?
How can we contact you?
Thanks, we've got your request
We’re excited to share our 5G connectivity solutions with you.
Check your email now for a confirmation message. Then a member of our team will send a personalised message within 1 business day to arrange a suitable time to have an in-depth one on one consultation.

5G Outdoor FW2000



Did you know?
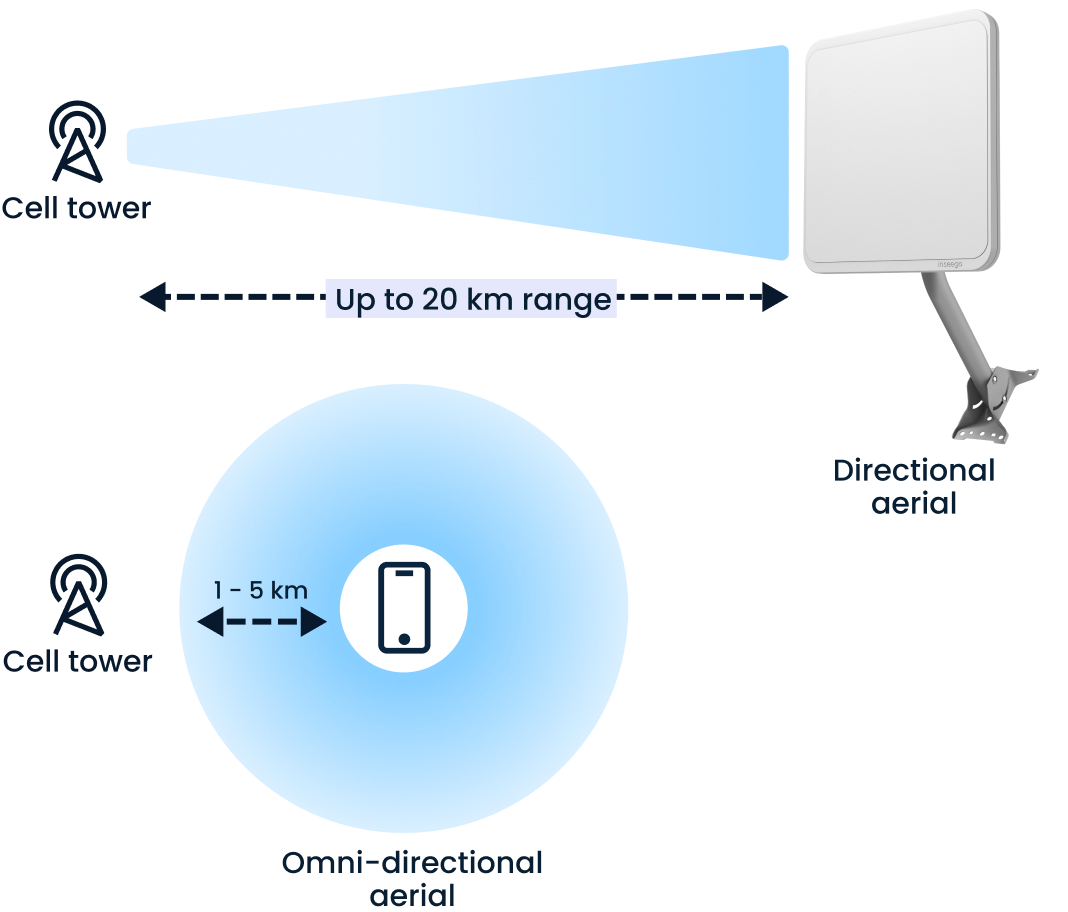

5G Outdoor FW2000

Did you know?
Our hugely experienced team are located across the USA.
We’ll connect you with the Inseego team member nearest to you.
What happens next?
We aim to contact you via email within 1 business day to arrange a suitable to time for a detailed discussion of your needs.

